
Next: Matching Multiple 3D Scans
Up: Automatic Model Refinement for
Previous: The Autonomous Mobile Robot
Range Image Registration
We use the well-known Iterative Closest Points (ICP) algorithm to
calculate a rough approximation of the transformation while the
robot is acquiring the 3D scans. The ICP algorithm calculates
iteratively the point correspondence. In each iteration step, the
algorithm selects the closest points as correspondences and
calculates the transformation (
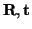 ) for minimizing the
equation
) for minimizing the
equation
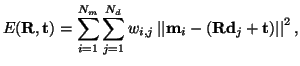 |
|
|
(1) |
where 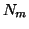 and
and 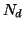 , are the number of points in the model set
, are the number of points in the model set
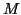 or data set
or data set 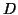 , respectively and
, respectively and 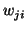 are the weights
for a point match. The weights are assigned as follows:
are the weights
for a point match. The weights are assigned as follows:
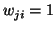 , if
, if 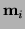 is the closest point to
is the closest point to 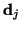 within a close
limit,
within a close
limit,
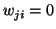 otherwise.
It is shown that the iteration terminates in a
minimum (5). The assumption is that in the last
iteration step the point correspondences are correct.
In each iteration, the transformation is calculated by the
quaternion based method of Horn (14).
otherwise.
It is shown that the iteration terminates in a
minimum (5). The assumption is that in the last
iteration step the point correspondences are correct.
In each iteration, the transformation is calculated by the
quaternion based method of Horn (14).
Subsections
root
2003-08-06