

Next: Object Classification
Up: The Autonomous Mobile Robot
Previous: The Kurt3D Robot Platform
The AIS 3D Laser Range Finder
The AIS 3D laser range finder (Figure 1, top middle)
[#!ICAR2003!#,#!ISR2001!#] is built on the basis of a 2D range
finder by extension with a mount and a standard servo motor. The
2D laser range finder is attached in the center of rotation to
the mount for achieving a controlled pitch motion. The servo is
connected on the left side (Figure 1, top
middle). The 3D laser scanner operates up to 5h (Scanner: 17 W,
20 NiMH cells with a capacity of 4500 mAh, Servo: 0.85 W, 4.5 V
with batteries of 4500 mAh) on one battery pack.
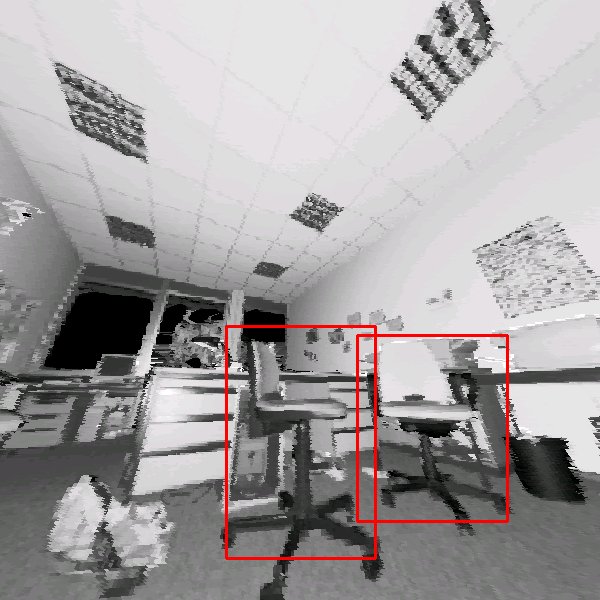
Figure:
Top row: The autonomous mobile robot Kurt3D equipped
with the 3D scanner. The AIS 3D laser range finder. Its technical
basis is a SICK 2D laser range finder (LMS-200). Top Right:
Scanned scene as point cloud (viewing pose 1 meter behind scan
pose). Reflectance values (distorted view: One scan line of the
figure corresponds to a slice of the 2D scanner
[#!ISR2001!#]). Bottom row: Input images used for object
learning (negative and positive examples for learing the object
``office chair''). Undistorted rendered
view as reflectance and depth image (range values are encoded by
grey values).
|
|
The area of
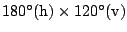 is scanned with different horizontal (181, 361, 721 pts.) and
vertical (210, 420 pts.) resolutions. A plane with 181 data
points is scanned in 13 ms by the 2D laser range finder (rotating
mirror device). Planes with more data points, e.g., 361, 721,
duplicate or quadruplicate this time. Thus, a scan with 181
is scanned with different horizontal (181, 361, 721 pts.) and
vertical (210, 420 pts.) resolutions. A plane with 181 data
points is scanned in 13 ms by the 2D laser range finder (rotating
mirror device). Planes with more data points, e.g., 361, 721,
duplicate or quadruplicate this time. Thus, a scan with 181
 210 data points needs 2.8 seconds. In addition to the
distance measurement, the 3D laser range finder is capable of
quantifying the amount of light returning to the scanner. Figure
1 (top right) shows a scanned scene as point cloud
with a viewing pose one meter behind the scan pose, and the
reflectance image (bottom left) of this scene. After scanning
the 3D data points are projected by an off-screen
OpenGL-based rendering module onto an image plane to
create a 2D images. The camera for this projection is located in
the laser source, thus all points are uniformly distributed and
enlarged to remove gaps between them on the image plane. Figure
1 (bottom row) shows a reflectance images and
rendered depth images, with distances encoded with grey values.
210 data points needs 2.8 seconds. In addition to the
distance measurement, the 3D laser range finder is capable of
quantifying the amount of light returning to the scanner. Figure
1 (top right) shows a scanned scene as point cloud
with a viewing pose one meter behind the scan pose, and the
reflectance image (bottom left) of this scene. After scanning
the 3D data points are projected by an off-screen
OpenGL-based rendering module onto an image plane to
create a 2D images. The camera for this projection is located in
the laser source, thus all points are uniformly distributed and
enlarged to remove gaps between them on the image plane. Figure
1 (bottom row) shows a reflectance images and
rendered depth images, with distances encoded with grey values.


Next: Object Classification
Up: The Autonomous Mobile Robot
Previous: The Kurt3D Robot Platform
root
2004-03-04
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{kurt3d}](img2.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{3d-laser}](img3.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{scene_points}](img4.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{scene_undist_dist}](img7.png)


![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{kurt3d}](img2.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{3d-laser}](img3.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{scene_points}](img4.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{scene_undist_dist}](img7.png)


![]() is scanned with different horizontal (181, 361, 721 pts.) and
vertical (210, 420 pts.) resolutions. A plane with 181 data
points is scanned in 13 ms by the 2D laser range finder (rotating
mirror device). Planes with more data points, e.g., 361, 721,
duplicate or quadruplicate this time. Thus, a scan with 181
is scanned with different horizontal (181, 361, 721 pts.) and
vertical (210, 420 pts.) resolutions. A plane with 181 data
points is scanned in 13 ms by the 2D laser range finder (rotating
mirror device). Planes with more data points, e.g., 361, 721,
duplicate or quadruplicate this time. Thus, a scan with 181
![]() 210 data points needs 2.8 seconds. In addition to the
distance measurement, the 3D laser range finder is capable of
quantifying the amount of light returning to the scanner. Figure
1 (top right) shows a scanned scene as point cloud
with a viewing pose one meter behind the scan pose, and the
reflectance image (bottom left) of this scene. After scanning
the 3D data points are projected by an off-screen
OpenGL-based rendering module onto an image plane to
create a 2D images. The camera for this projection is located in
the laser source, thus all points are uniformly distributed and
enlarged to remove gaps between them on the image plane. Figure
1 (bottom row) shows a reflectance images and
rendered depth images, with distances encoded with grey values.
210 data points needs 2.8 seconds. In addition to the
distance measurement, the 3D laser range finder is capable of
quantifying the amount of light returning to the scanner. Figure
1 (top right) shows a scanned scene as point cloud
with a viewing pose one meter behind the scan pose, and the
reflectance image (bottom left) of this scene. After scanning
the 3D data points are projected by an off-screen
OpenGL-based rendering module onto an image plane to
create a 2D images. The camera for this projection is located in
the laser source, thus all points are uniformly distributed and
enlarged to remove gaps between them on the image plane. Figure
1 (bottom row) shows a reflectance images and
rendered depth images, with distances encoded with grey values.