
Next: Conclusions
Up: Automatic Classification of Objects
Previous: The Cascade of Classifiers
Several experiments have been done to evaluate the performance of
the proposed approach with two different kinds of images, namely,
reflectance and depth images. Both types are acquired by the AIS
3D laser range finder and are light invariant. Figure
1 shows two examples of the training data
set. Around 200 representation of an ``office chair'' were taken
in addition to a wide variety of negative examples without any
chair, e.g., the scene given in Figure 1. The
detection starts with a classifier of size 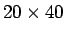 pixels. The image is searched from top left to bottom right by
applications of the cascade. To detect objects on larger scales,
the detector is rescaled. An advantage of the Haar-like features
is that they are easily scalable. Each feature requires only a
fixed number of look-ups in the integral image, independent of
the scale. Time-consuming picture scales are not necessary to
achieve scale invariance.
pixels. The image is searched from top left to bottom right by
applications of the cascade. To detect objects on larger scales,
the detector is rescaled. An advantage of the Haar-like features
is that they are easily scalable. Each feature requires only a
fixed number of look-ups in the integral image, independent of
the scale. Time-consuming picture scales are not necessary to
achieve scale invariance.
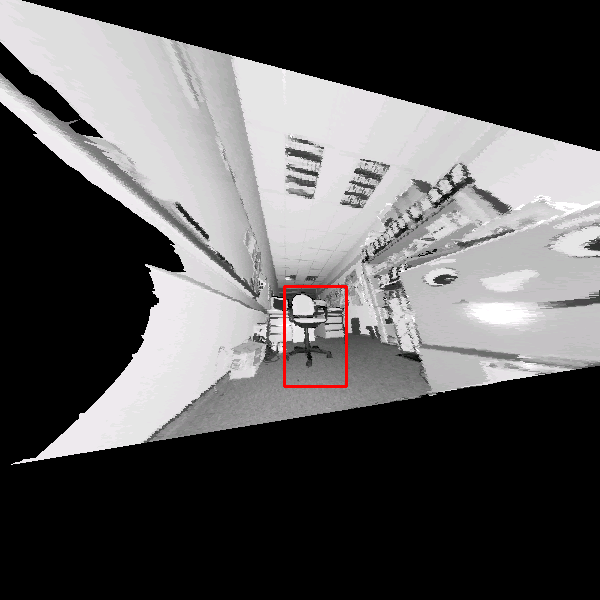
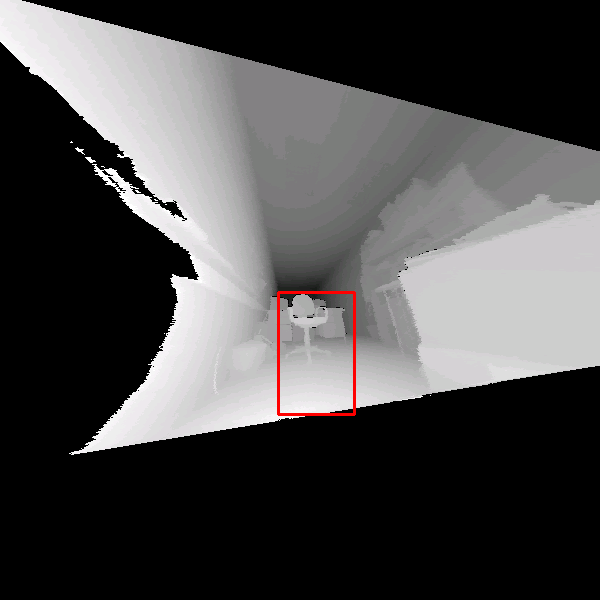
Table 1 summarizes the results of the object
detection algorithm with a test data set of 30 scans that are not
used for learning. Some examples of the detection of an ``office
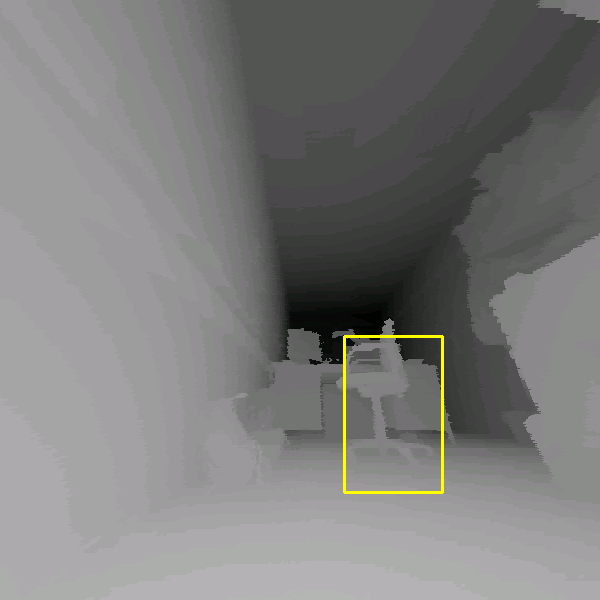
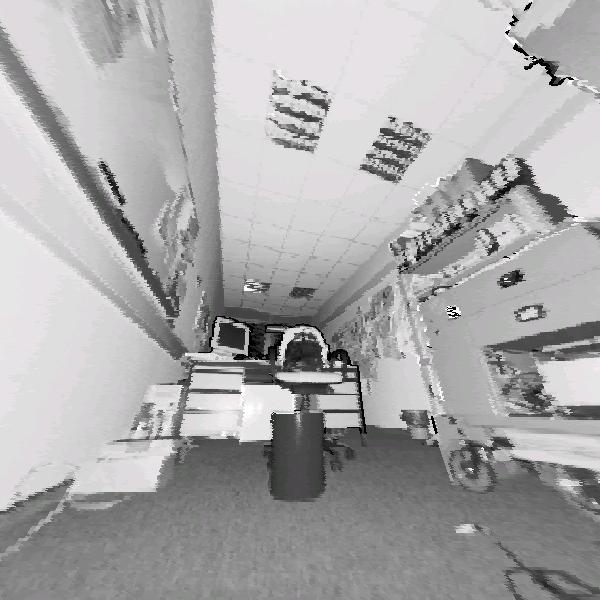
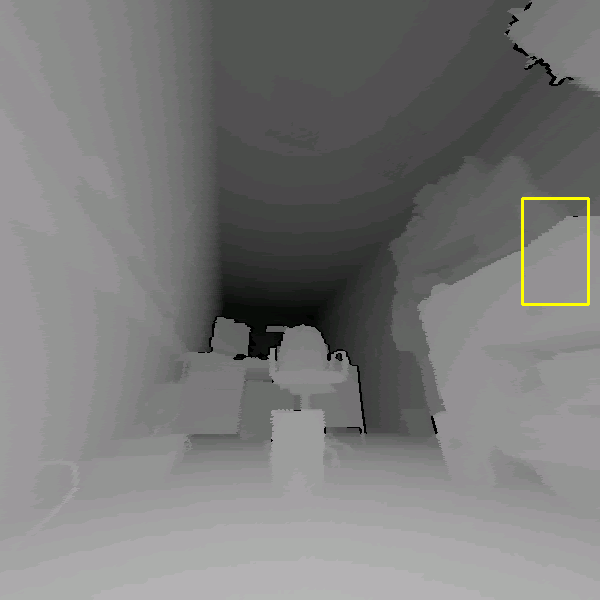
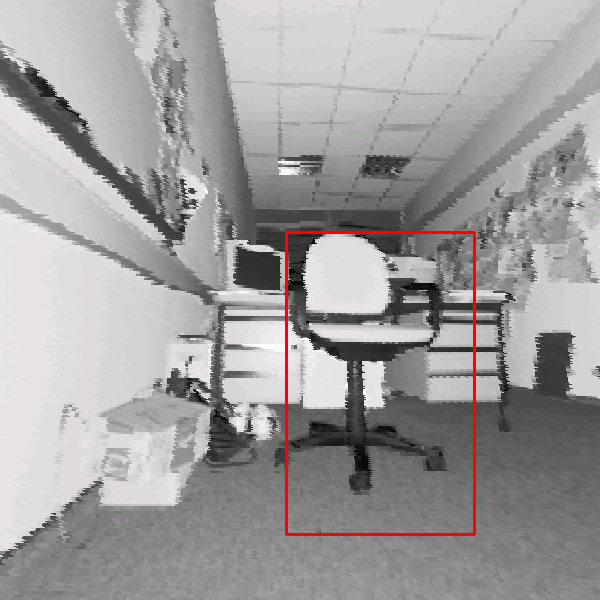
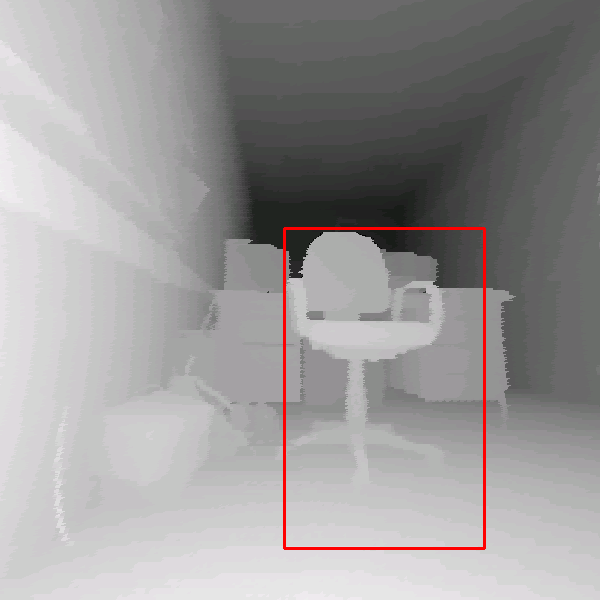
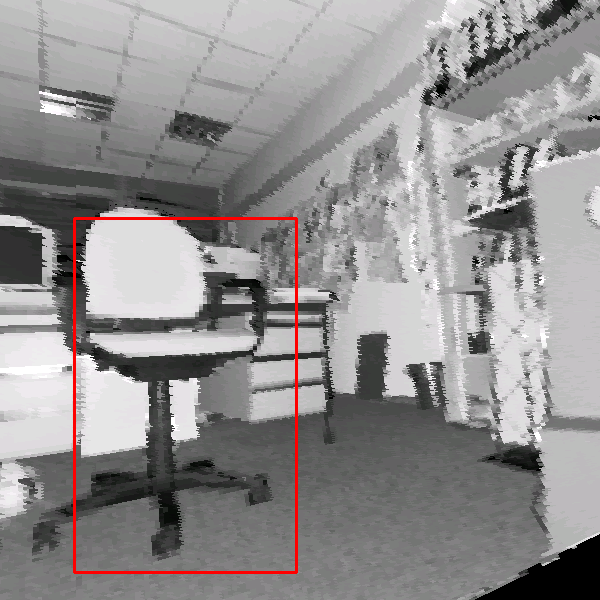
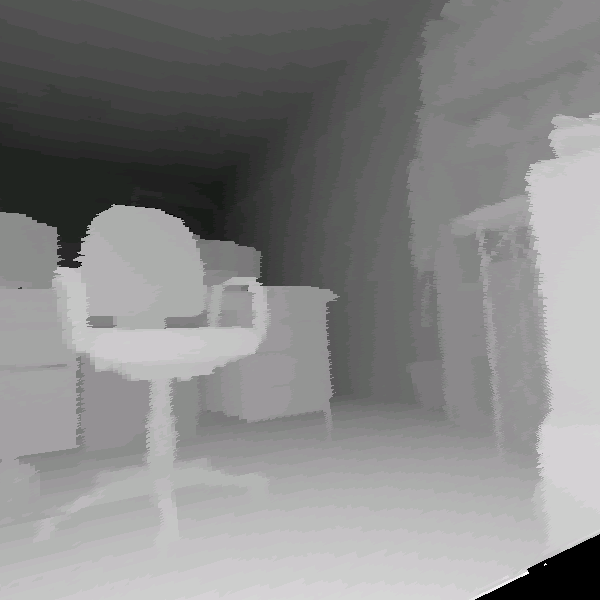
chair'' in 3D scans are given in Figure 4. Hits as
well as missed and false alarms are documented. In addition, the
figure presents the scaling feature of the detector, since the
last two images of the third row were rendered with a wide apex
angle of the virtual projection camera. In addition some results
of the proposed object detection with partial occlusions are shown
(bottom row). The cascade in Figure 3 presents the
first three stage classifiers for the object ``office chair''
using depth values. One main feature is the horizontal bar (first
stage).
The experiments inspired us to combine the cascades of the depth
and reflectance images. Figure 5 shows two
variants of the combination: Either the two cascades run
interleaved (left) or serial (right) and represent a logical
``and''. The joint cascade decreases the false detection rate
close to zero. To avoid the reduction of the hit rate, 6
different off-screen rendered images are used, where the virtual
camera is rotated, i.e., the rotation by the Euler angles
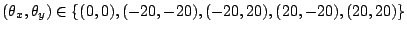 is applied. The 6th image is generated with a wide
apex angle of 150 deg.
is applied. The 6th image is generated with a wide
apex angle of 150 deg.
Table 1:
Number of stages versus hit rate and false
alarms. The last row shows the result of the combined
classifier for reflectance and depth images. A detection
including searching in the image using
the combined cascade with 15 + 15 stages needs 376ms
(Pentium-IV-2400).
|
number of |
hit rate |
false alarms |
|
stages |
reflect. img. |
depth img. |
reflect. img. |
depth img. |
|
15 |
0.9 |
0.866 |
0.067 |
0.067 |
|
30 |
0.867 |
0.767 |
0.067 |
0.033 |
|
(15 + 15) applied to 6 img. |
0.967 |
0.0 |
Figure:
Detection results using the classifier with 15
stages. The classified object is marked by a rectangle. Top
row: Detection in reflectance and depth images. Second row: A
false classification in a reflectance image is not present in
the depth image (left). An object might be detected with
different detector scales (right). Third row: Rotated images
(left) and wide angle projections (right). Bottom row:
Detection results under presence of partial occlusions. Small
changes of the viewpoint are tolerated, e.g., a view from the
side (left). If the main features are occluded the object
detection fails (right).
|
|


Next: Conclusions
Up: Automatic Classification of Objects
Previous: The Cascade of Classifiers
root
2004-03-04
![]() is applied. The 6th image is generated with a wide
apex angle of 150 deg.
is applied. The 6th image is generated with a wide
apex angle of 150 deg.


![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_i23}](img41.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_d23}](img42.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_i14}](img43.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_d14}](img44.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_i13}](img45.png)
![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{res_d13}](img46.png)


![\includegraphics[width=38mm,height=38mm]{occ_i1}](img47.png)


