After matching multiple 3D scans, errors have accumulated and
loops would normally not be closed. Our algorithm automatically
detects a to-be-closed loop by registering the last acquired 3D
scan with earlier acquired scans. Hereby we first create a
hypothesis based on the maximum laser range and on the robot
pose, so that the algorithm does not need to process all previous
scans. Then we use the octree based method presented in section
3.1 to revise the hypothesis. Finally, if a registration
is possible, the computed error, i.e., the transformation (![]() ,
, ![]() ) is distributed over all 3D scans. The respective part
is weighted by the distance covered between the scans, i.e.,
) is distributed over all 3D scans. The respective part
is weighted by the distance covered between the scans, i.e.,
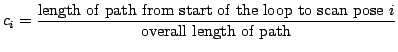
The quaternion describes a rotation by an axis
![]() and an angle
and an angle 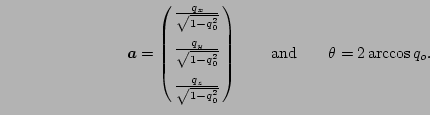 that are computed by
that are computed by
The angle 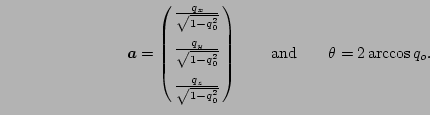 is distributed over all scans using the factor
is distributed over all scans using the factor
![]() and the resulting matrix is derived as [8]:
and the resulting matrix is derived as [8]:
The next step minimizes the global error.